반응형
선택 정렬(selection sort)
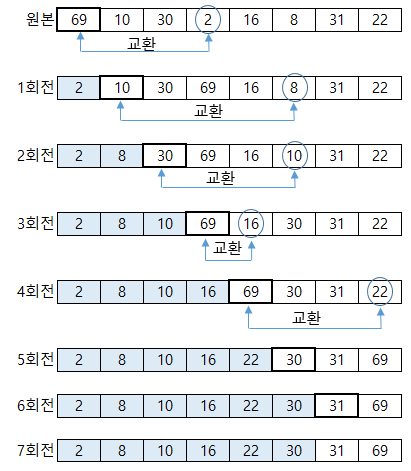
선택 정렬은 정렬되지 않은 데이터들에 대해 가장 작은 데이터를 찾아 가장 앞의 데이터와 교환해나가는 방식으로 정렬 과정을 수행합니다.
#include <stdio.h>
void print(int a[], int size) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void SelectionSort(int a[], int size)
{
int i, j, min, temp;
for (i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
{
min = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < size; j++)
{
if (a[j] < a[min]) min = j;
}
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[min];
a[min] = temp;
}
}
int main()
{
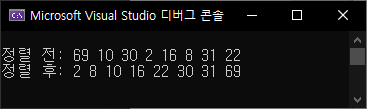
int list[8] = { 69, 10, 30, 2, 16, 8, 31, 22 };
int size = 8;
printf("\n정렬 전: ");
print(list, size);
SelectionSort(list, size);
printf("정렬 후: ");
print(list, size);
return 0;
}
다음 코드는 선택 정렬의 각 단계별 정렬 과정을 출력해 보는 예제입니다.
#include <stdio.h>
void print(int a[], int size) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void SelectionSort(int a[], int size)
{
int i, j, min, temp;
for (i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
{
min = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < size; j++)
{
if (a[j] < a[min]) min = j;
}
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[min];
a[min] = temp;
printf("\n[%d단계] ", i + 1);
for (t = 0; t < size; t++)
printf("%2d ", a[t]);
}
}
int main()
{
int list[8] = { 69, 10, 30, 2, 16, 8, 31, 22 };
int size = 8;
printf("\n정렬 전: ");
print(lsit, size);
SelectionSort(list, size);
return 0;
}
반응형
'C_C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (C언어) 10진수를 2진수로 변환, 배열 이용 (0) | 2022.10.05 |
|---|---|
| (C언어) qsort 함수를 이용한 숫자 정렬 (0) | 2022.10.04 |
| (C언어) 버블 정렬 Bubble Sort (0) | 2022.10.02 |
| (C언어) 로또 번호 생성: 중복되지 않은 수 (0) | 2022.10.02 |
| (C++) auto 키워드: 자동 타입 추론(automatic type deduction) (0) | 2022.10.02 |